Division
Eco-Plant Division GRP Pipe Extending to the World Beyond Korea.
FAQ
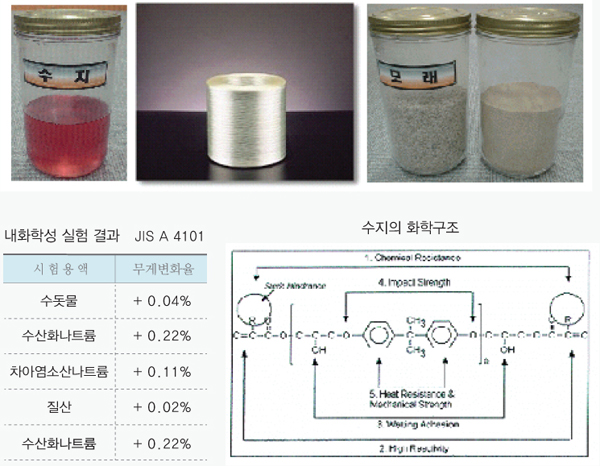
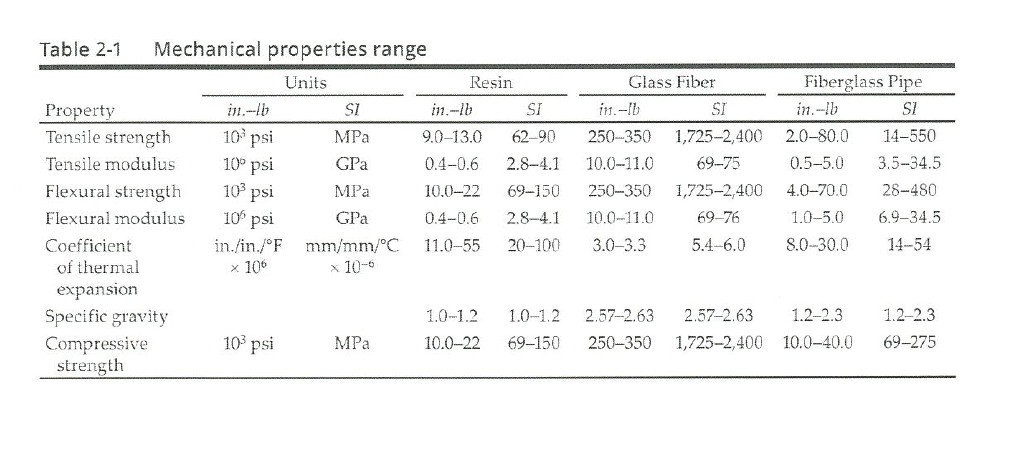
GRP pipes are made by mixing liquid plastic and glass fiber to form a glass fiber reinforced plastic (FRP/GRP) pipe. They have high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, making them resilient and compatible with other pipes. Additionally, they offer excellent watertightness.
Rigid pipes bear all loads, including soil and trucks, through their internal strength and do not allow deformation. If deformation occurs, the pipe is destroyed. Examples of rigid pipes include conduit, Hume pipe, PC pipe, VR pipe, and all pipes made of concrete. The foundation for rigid pipes may be sand or crushed stone, or a fixed foundation such as gravel or concrete may be used depending on the conditions.
Ductile pipes transmit all loads to the ground and can tolerate up to 5% strain without failing, making them more flexible than rigid pipes. Examples of ductile pipes include ductile cast iron pipe, steel pipe, PVC pipe, PE pipe, and glass fiber composite pipe, but not pipes made of concrete. The foundation for ductile pipes is typically made of free bearing sand, and a pile foundation may be installed depending on the conditions, according to the Sewerage Facility Standard of the Ministry of Environment.
Water pipe line (straight pipe): Hydraulic test pressure is 1.5 times the pressure grade (PN), similar to the test pressure of steel pipe
15 minutes for GRP pipe
Coated steel pipe maintains the pressure for 5 seconds.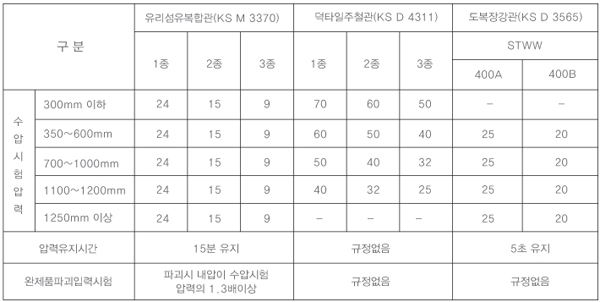
Pipeline (Connector) The joint watertightness test is used to evaluate the watertight performance of pipe joints under normal operating conditions. This test is conducted when laying a curved pipe through a bent pipe at the joint in the field. The eccentric load watertightness test evaluates the joint's performance when an eccentric load is applied due to soil loss or differential settlement under the pipe after it has been laid. The repeated pressure watertightness test assesses the joint's performance when water filling pressure is applied repeatedly. The negative pressure (-) watertightness test evaluates the joint's performance in preventing the inflow of external substances when negative pressure is created due to water intake or rapid interruption of pressurization.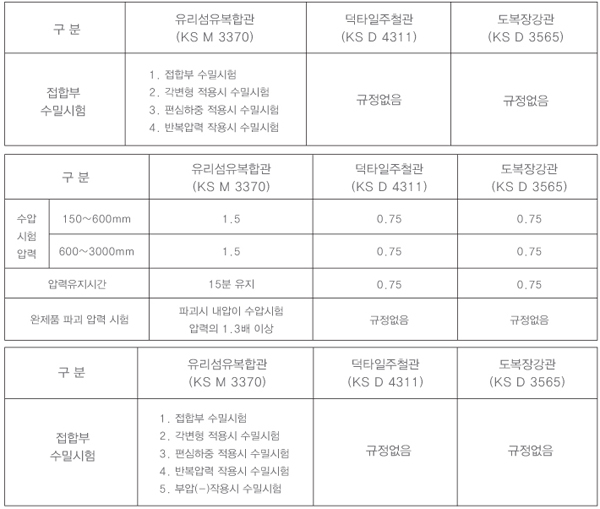
15 minutes for GRP pipe
Coated steel pipe maintains the pressure for 5 seconds.

Pipeline (Connector) The joint watertightness test is used to evaluate the watertight performance of pipe joints under normal operating conditions. This test is conducted when laying a curved pipe through a bent pipe at the joint in the field. The eccentric load watertightness test evaluates the joint's performance when an eccentric load is applied due to soil loss or differential settlement under the pipe after it has been laid. The repeated pressure watertightness test assesses the joint's performance when water filling pressure is applied repeatedly. The negative pressure (-) watertightness test evaluates the joint's performance in preventing the inflow of external substances when negative pressure is created due to water intake or rapid interruption of pressurization.

Despite its many advantages, the GRP pipe is not well-known. Recently, various types of pipes made from new materials have emerged to compensate for the drawbacks of existing pipes. However, the GRP pipe has made rapid progress in just a few years since its introduction. It has been recognized as an excellent product, obtaining patents and being designated as a new technology and excellent product.
In 2005, the GRP pipe was applied to approximately 60 water pipeline construction sections (totaling 112 km), about 120 sewer pipe construction sections (238 km), and around 200 manhole construction sections (for a total of 4,780 manholes) due to its exceptional performance.
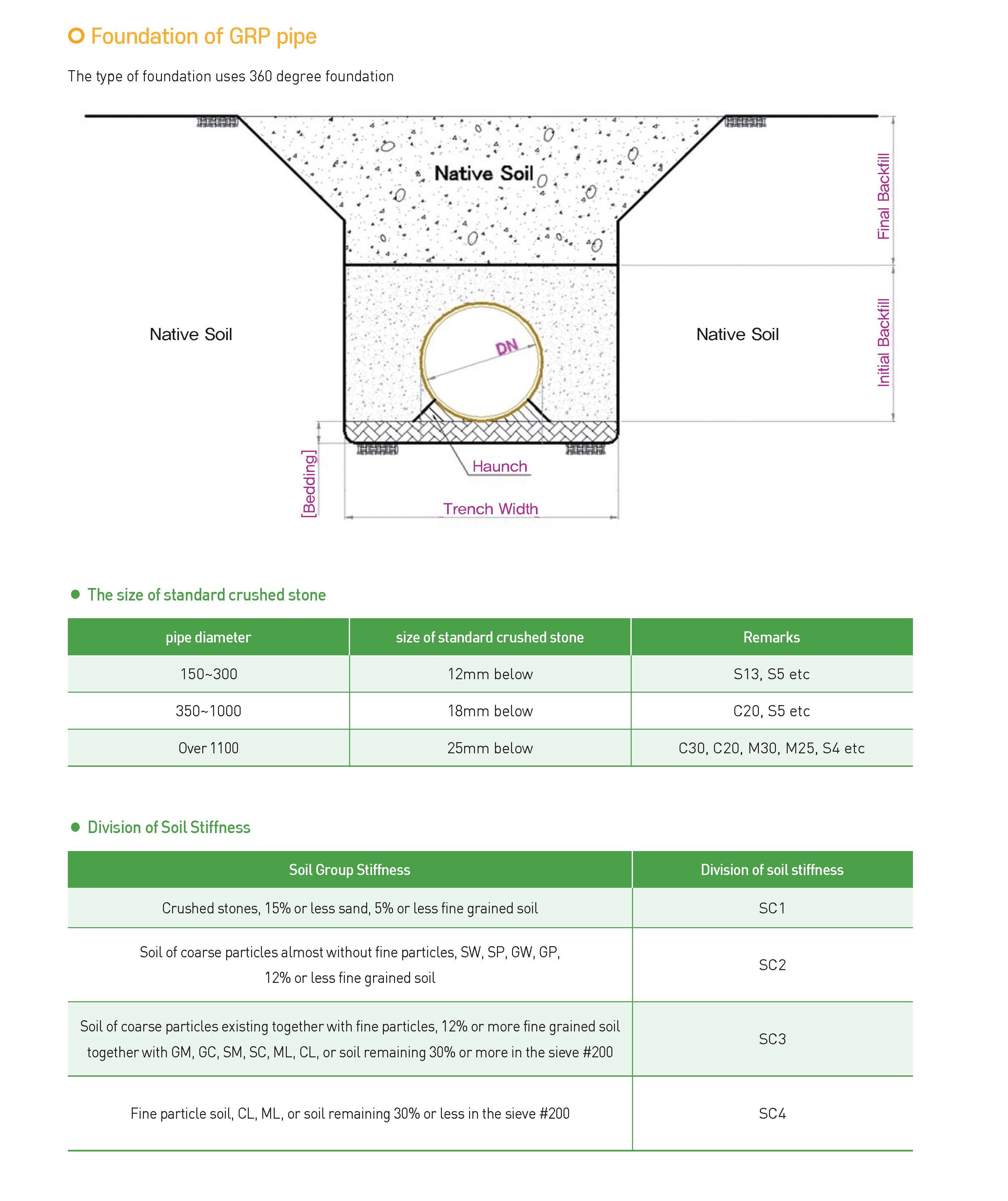
The standards for installing the protection structure of GRP pipe are as follows. In the fittings (bend pipes, T-shaped pipes) where pressure is applied, it is designed in the same way as ductile cast iron pipes (Civil Design Standards of Korea Water Resources Corporation). When a pipe crosses a river, it is installed regardless of the pipe type (cast iron/steel pipe) because of the possibility of soil loss, and when a pipe crosses a road with a buried depth of 1.0m or less, it is installed to protect the pipe from the impact caused by the load of the truck. When a pipe is installed without being buried underwater, it is installed regardless of the type of pipe because of the possibility of pipe movement caused by ocean currents.
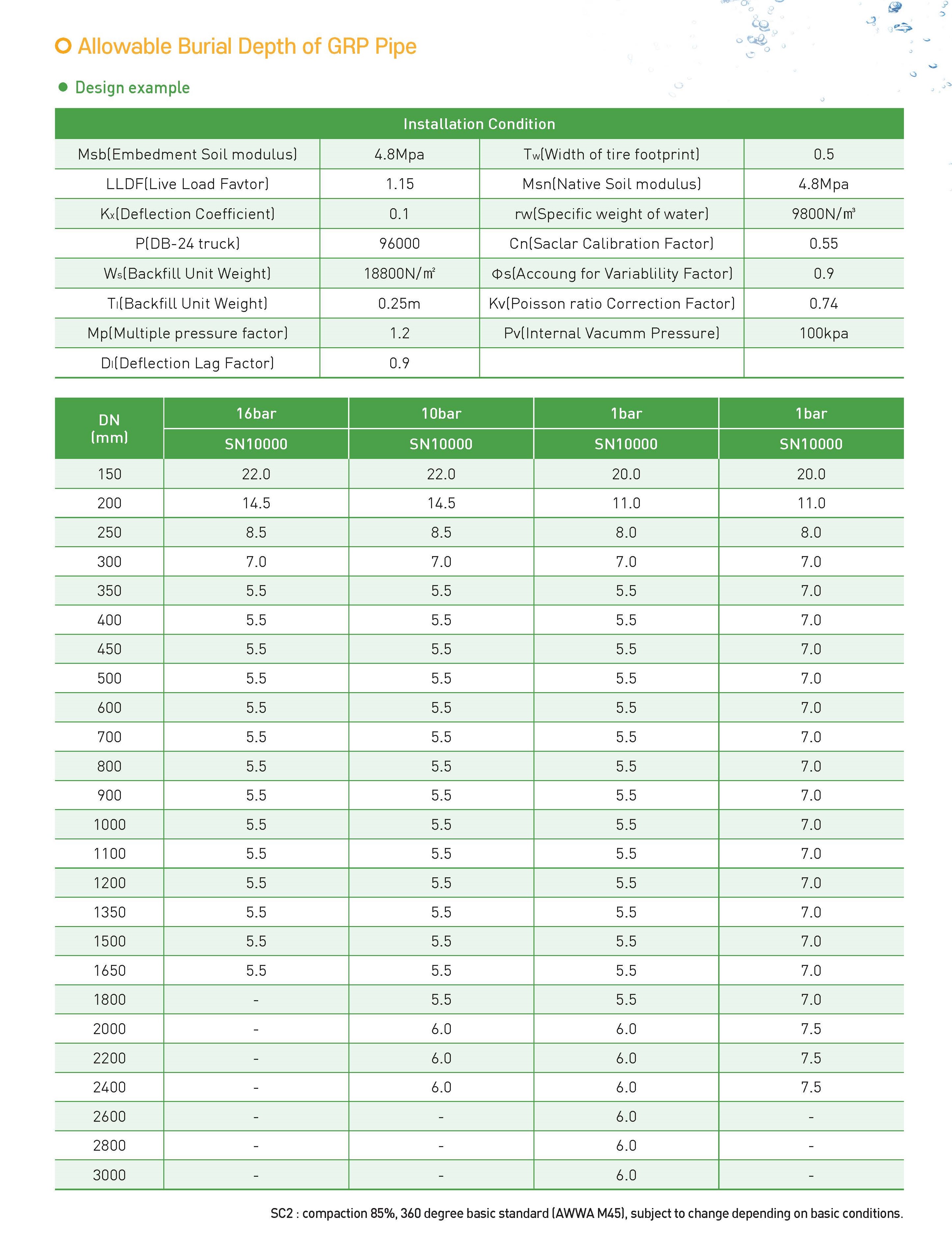
Working pressure, which is the pressure that actually acts on the pipeline, is the sum of the static pressure and the dynamic pressure (water filling pressure), and is specified as PN16≥(static water pressure + dynamic water pressure)/1.4 in AWWA M 45 (American Water and Wastewater Association). The test pressure is used at the factory to manage the pressure resistance of the product, and is 32kg/cm2 for PN16.
Guaranteed water pressure is calculated as 70% of the burst water pressure in the cast iron pipe (excerpt from the cast iron pipe handbook), and there is no regulation for PN16.
Burst pressure is tested at 76.5~75kg/cm2 for PN16? for the purpose of discovering defects in casting of cast iron pipe (excerpt from cast iron pipe handbook).
Hydrostatic pressure refers to the pressure that is constantly applied to a pipe when water passes through the pipe normally.
Dynamic water pressure (or water filling pressure) refers to the instantaneous increase in pressure that occurs when the pump is started or stopped, or when the valve is opened or closed, and is about 3 to 5 kg/cm2.
Guaranteed water pressure is calculated as 70% of the burst water pressure in the cast iron pipe (excerpt from the cast iron pipe handbook), and there is no regulation for PN16.
Burst pressure is tested at 76.5~75kg/cm2 for PN16? for the purpose of discovering defects in casting of cast iron pipe (excerpt from cast iron pipe handbook).
Hydrostatic pressure refers to the pressure that is constantly applied to a pipe when water passes through the pipe normally.
Dynamic water pressure (or water filling pressure) refers to the instantaneous increase in pressure that occurs when the pump is started or stopped, or when the valve is opened or closed, and is about 3 to 5 kg/cm2.
Sudden water pressure surges caused by the sudden opening and closing of valves, the release of air from air valves, and the starting and stopping of pumps can lead to excessive pressure, pipe vibration, and damage to pipes and fittings.
According to a design excerpt from AWWA M45 comparing GRP pipes and metal pipes, the modulus of elasticity of GRP pipes is relatively lower, causing the pressure wave to gradually decay while passing through the pipe due to the magnetic damping effect. In contrast, the amplitude of the pressure wave is larger in metal pipes due to the high modulus of elasticity of the material, making GRP pipes a safer option.
There are two buoyancy problems.
If the pipe is more than 3/4 (75%) full of water, no buoyancy will appear.
Second, if there is no water inside the pipe and the outside is completely submerged during construction, according to the GRP pipe handbook, it is said to be safe if it is backfilled as much as the diameter (D).(Safety factor 2.0)
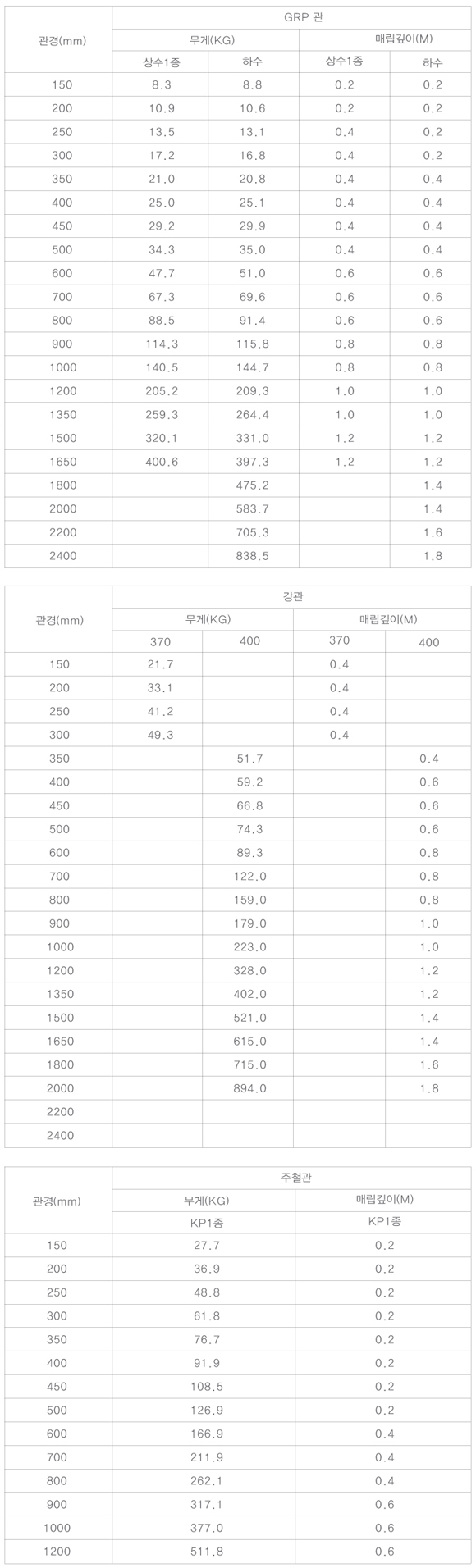
Looking at the table below, you can see that GRP pipes generate buoyancy similarly to steel pipes or cast iron pipes.
If the pipe is more than 3/4 (75%) full of water, no buoyancy will appear.
Second, if there is no water inside the pipe and the outside is completely submerged during construction, according to the GRP pipe handbook, it is said to be safe if it is backfilled as much as the diameter (D).(Safety factor 2.0)
Looking at the table below, you can see that GRP pipes generate buoyancy similarly to steel pipes or cast iron pipes.

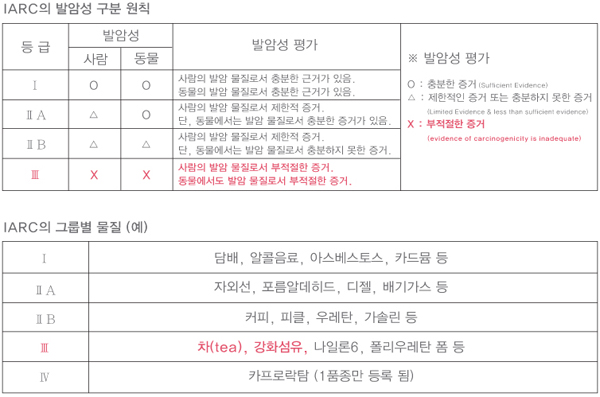
The reinforcing fiber, which is the primary material of reinforced plastic pipes, was evaluated as Level III by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) in October 2001, indicating that it is absolutely harmless to humans and animals.
It belongs to a higher group than urethane and styrene and has been proven to have the same level of safety as nylon and tea. In fact, this can be considered an international safety declaration for reinforcing fibers.
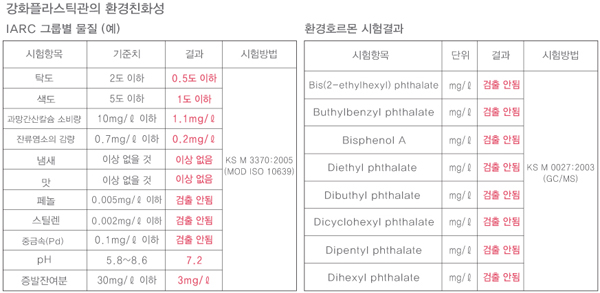
Moreover, the main component of the reinforcing fiber is silica sand (SiO2), which is chemically safe and does not undergo chemical changes in various types of glass, optical fibers, ceramics, acids, alkalis, and various solvents. It is also used as a raw material for containers for various foods, beverages, medicines, and samples.
It belongs to a higher group than urethane and styrene and has been proven to have the same level of safety as nylon and tea. In fact, this can be considered an international safety declaration for reinforcing fibers.
Moreover, the main component of the reinforcing fiber is silica sand (SiO2), which is chemically safe and does not undergo chemical changes in various types of glass, optical fibers, ceramics, acids, alkalis, and various solvents. It is also used as a raw material for containers for various foods, beverages, medicines, and samples.


Contact information by region
Contacts for water supply and sewage
| Region | Contact person | Extension | FAX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seoul | Bae Byung-jun | 031-8086-4405 | 031-8086-4480 | |
| Incheon | Kim Hong-soo | 031-8086-4404 | 031-8086-4480 | |
| Gyeonggi-do | Bae Byung-jun | 031-8086-4405 | 031-8086-4480 | |
| Kim Hong-soo | 031-8086-4404 | 031-8086-4480 | ||
| Chungcheongnam-do | Son Young-tae | 055-960-3276 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Chungcheongbuk-do | Son Young-tae | 055-960-3276 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Daejeon | Son Young-tae | 055-960-3276 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Jeollabuk do | Kim Ji-min | 055-960-3278 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Gwangju | Kim Ji-min | 055-960-3278 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Jeollanam-do | Kim Ji-min | 055-960-3278 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Gangwon-do | Bae Byung-jun | 031-8086-4405 | 031-8086-4480 | |
| Gyeongsangnam-do | Kim Geo-rak | 055-960-3273 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Daegu | Kim Geo-rak | 055-960-3273 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Gyeongsangnam-do | LeeSang-jeong | 055-960-3272 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Kim Hyun-soo | 055-960-3274 | 055-960-3289 | ||
| Son Young-tae | 055-960-3276 | 055-960-3289 | ||
| Ulsan | Kim Hyun-soo | 055-960-3274 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Busan | Lee Sang-dong | 055-960-3275 | 055-960-3289 | |
| Jeju-do | Son Young-tae | 055-960-3276 | 055-960-3289 | |
1) Plant (electric power, chemical engineering, marine) 2) Environment 3) FRP structure